Mobile Agriculture Education Science Lab
The Mobile Agriculture Education Science Lab is an educational experience for elementary and middle school students.
The Mobile Agriculture Education Science Lab is a 40-foot mobile classroom that travels across the state of Pennsylvania bringing an interactive field trip style experience directly to schools and students in grades K-8. The Mobile Ag Lab is equipped with over 30 STEM-based science experiments and lessons, a certified teacher, and all the supplies needed for a hands-on learning experience. Each science experiment is designed to emphasize a different aspect of agriculture, including Pennsylvania’s commodities, the environment, biotechnology, food and fiber. While on our lab, students work cooperatively to solve a problem as they form a hypothesis, collect data and draw conclusions while focusing on the scientific method. Each lesson on the Mobile Ag Lab focuses on increasing student knowledge on the importance of agriculture and its impact on their daily lives.






Lesson Extensions
Walk Through
Vocabulary
Print All
General
- agriculture – farming; the occupation, business, or science of cultivating the land, producing crops, and raising livestock in order to provide food and products
- by-product – something of value produced during the making of another product
- conclusion – to bring to a close; to deduce by
- control – to regulate or restrain
- data – information; facts or figures used in analysis
- hypothesis – an educated scientific guess
- observation – to notice or record results in a science experiment
- procedure – a series of actions or steps completed in a certain order
- product – something that is manufactured or refined for sale
- properties – a characteristic or quality of something
- scientific method – a process that scientists use to study and learn about the world around them; a tool that scientists use to find the answer to questions by following a series of steps:
1. Identify Problem
2. Form a Hypothesis
3. Test the Hypothesis
4. Collect and Analyze data
5. Make Conclusions
- variable – something able to change or vary
Elementary
Colorful Bean
- biodegradable – readily decomposed or broken down through bacterial action
- hydrogenated – to treat a liquid vegetable oil with hydrogen and convert it into a solid fat
- non-renewable – a resource or product that cannot be renewed or recycled
- petroleum – a thick, dark, flammable liquid that occurs naturally below the surface of the earth and is processed into such products as natural gas, gasoline, kerosene, and fuel oils
- renewable – a resource able to be restored or made new again
Mighty Smooth Bean
- absorption – the process of taking in of a liquid or absorbing
- chemical change – to bring about a change in the chemical makeup of a substance
- embryo – the early developmental stage of an animal or plant
- roots – the base of a plant that usually grows underground
- seed coat – the protective outer covering of a seed
- stored sugars – food within a seed put away for future use
Glue from Milk
- casein – a milk and cheese protein used in foods and manufacturing plastics and adhesives
- curds – coagulated milk; to change from a liquid state to a thick, soft mass
- peel strength – the stress an adhesive can bear without tearing apart when it is pulled back along the surface
- shear strength – the stress an adhesive can bear without tearing apart when the stress is along the bond (pulling sideways)
- tensile strength – the stress an adhesive can bear without pulling apart when the stress is at a right angle to the bond (pulling apart)
- viscosity – property of fluids that causes them not to flow easily
- whey – a clear liquid that separates from the curd when milk is curdled
Cream to Butter
- agitation – to shake or move sharply and irregularly
- fat content – the amount per serving of dietary fat
- homogenized – milk that has been processed to break up fat globules and distribute them evenly throughout
- nutrition label – a source used to determine the amount of nutrition in a food product
How Well Do You Wash?
- bacteria – a division of microorganisms that cause various diseases
- friction – the rubbing of a surface or object against another
- germs – any microorganism, especially one that is harmful
- percentage – parts per hundred: a fraction or ratio out of 100
Snack Attack
- contamination – to pollute; to make impure
- fat – oily animal substance
- healthy – soundness of body or mind
- ingredients – the elements in a mixture
- nutrition labels – information found on all foods to indicate calories, fat, etc.
- processed – a series of changes in developing or manufacturing a product
Tree Story
- cambium – cell layer under bark of plants and trees from which new wood and bark grow
- dendrochronology – tree ring dating; an absolute dating technique using the growth rings of trees
to determine the age of a stand of trees - heartwood – the skeletal system of a tree made of dead sapwood that appears a darker color than new sapwood
- increment borer – a tool used by forestry workers to sample a tree and determine the age of the tree without cutting down the tree
- inner bark – the digestive system of a tree made of live phloem cells that carry the
sugar/food made in the leaves throughout the tree - outer bark – the skin of the tree made of dead phloem cells that split and shift in various patterns special to each tree
- phloem – plant tissue made of live cells
- sapwood – the circulatory system of a plant or tree made of xylem cells that carry minerals and water throughout the tree
- xylem – the woody vascular tissue of a plant or tree
Where’s the Juice?
- contamination – the action of making something impure
- nutritious – food with nourishing value
Pigment Power
- acid – a chemical substance that neutralizes alkalis
- base – a substance that reacts with an acid to form a salt and water
- chemical reaction – a reaction that happens when two or more molecules interact and something happens
- control – in an experiment, a substance not tested that remains in its original form
- neutral – having no strongly marked characteristics or features
- phytochemicals – naturally occurring plant chemicals that fight disease
Fungi Fun
- animals – multi-celled living things that consume organic matter as food for energy and are characterized by voluntary movement
- cap – the button or umbrella-like part of the mushroom that supports the reproduction process for the mushroom
- carbon dioxide – colorless, odorless gas that is produced when people and animals breathe out
- chlorophyll – green pigment present in plants that absorbs sunlight to make energy for the photosynthesis process
- classification – the process of organizing something according to shared qualities or characteristics. Classifications of living things start with categories called kingdoms
- flower – the part of the plant that is often brightly colored and allows for reproduction to occur
- fungus – a special classification of living things that lacks chlorophyll and vascular tissue that feeds on organic matter and reproduces by spores
- gills – the vertical plates arranged radially on the underside of mushroom caps that form spores
- kingdom – categorizing living things by the way they absorb, ingest, or produce food
- leaves – a flat green part that grows in various shapes from the stems and branches of a plant or tree and whose main function is photosynthesis
- mycelium – an underground mass of interwoven filaments that collect the nourishment for the mushroom
- oxygen – colorless, odorless gas that is necessary for the survival of living things
- photosynthesis – the process by which green plants use chlorophyll and sunlight to make foods from carbon dioxide and water that generates oxygen
- pistil – the long central part of the flower that produces the seeds
- plants – multi-celled living things that produce their own from inorganic matter through photosynthesis
- root – underground part of the plant that anchors the plant and absorbs nutrients and water for the plant
- seed – part of the plant, usually contained in the fruit of the plant, from which a new plant can grow
- spores – tiny, tiny parts of the mushroom that produce new mushroom caps from the spores
- stem – main body of a plant that carries water and nutrients for the plant and supports the leaves, flowers, and fruit of the plant
- stipe – short stem-like part of the fungus that supports the cap
- vascular tissue – the system of tubes that carry resources (water, nutrients, and food) throughout the plant
- yeast – a single-celled organism that converts sugar to alcohol and carbon dioxide
Environmentally Friendly Farmer – My EFF
- buffer zones – strips of grass, trees, or shrubs that are planted along the edges of fields and/or waterways to decrease the amount of soil erosion (both by wind and water) and water pollution
- corn – a tall green plant that produces large grains, or kernels, set in rows on a cob that yield numerous products that are highly valued for both human and animal consumption
- cover crops – a crop that is planted between growing seasons to protect and enrich the soil
- crops – plant or plant products that are grown by farmers
- erosion – gradual breaking down
- fencing – a barrier enclosing or bordering a field or yard, usually made fop sots and wire, used to prevent entrance or confine animals to a particular space
- manure pit – a structure on livestock farms for the collection and storage of manure
- natural resources – materials or substances that are found in nature and are necessary or useful to humans
- non-renewable – a resource or product that cannot be renewed or recycled
- renewable – a resource able to be restored or make new again
- shrubs – a woody plant that is smaller than a tree and has several main stems starting at or near the ground
- silo – a tower on a farm used to store food (grain or grass) for farm animals
- soil – black or dark brown upper layer of earth consisting of a mixture of organic remains, clay, and rock particles in which plants grow
- soybeans – a bushy plant in the legume family that produces a seed that contains a large amount of protein and is used as food sources for both humans and livestock
- wheat – a plant with thin yellow stalks that produces a small grain that is important in animal feeds and from which flour is made to produce breads, baked goods, pasta
Magical Bean
- biodegradable – decomposed or broken down through bacterial action
- renewable – a substance that can be made renewed or used again
- nonrenewable – a substance that can not be renewed or used again
- soybean – a bushy plant in the legume family that produece a seed that contains a large amount of protein and is used as food sources for both animals and livestock
- legumes – legume plants have trifoliate leaves ( leaves with three parts). Peas, beans, peanuts, and clover are all legumes
- nodules – found on the roots of the plant. Home to microbes that convert nitrogen in the air into soil nitrogen
- harvest – the process of gathering crops
- combine – a large machine that is used on farms to harvest grains by cutting, sorting, and cleaning grain in the field
- soybean oil – viscous liquid extracted from the seeds of the soybean
- soy meal – powdery edible part of the soybean made by grinding
- soy lecithin – fat that is essential in the cells of the body and can be found in many foods
- emulsifier – a substance that stabilizes processed foods, and allows ingredients to mix smoothly
No Soil? Now What?
- uninhabitable – areas of land that are not suitable for people to live or grow crops (deserts, montains, polar regions)
- habitable – a place suitable for living
- arable – land suited for growing crops
- non arable – land where people can live, but crops cannot be grown because it is too rocky, hot, wet, or it has been developed
- hydroponic – the process of growing plants without soil
- nutrients – anything that nourishes a living thing; a substance or material used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce
- nitrogen – keeps plants green and healthy
- phosphorous – helps plants grow strong and healthy roots
- potassium – helps plants fight disease
- fertilizer – a chemical or natural substance added to soil to increase its fertility, or ability to grow plants
- aerate – to introduce air into a material
- rockwool – a lightweight material made from spinning melted basaltic rock into fine fibers that are then formed into cubes or blocks
Middle School
Steering Through the Chute
- livestock – domesticated animals raised to produce labor and commodities such as eggs, milk, meat, etc.
- natural shelters – shade from trees, access to barns
- sustainable grazing – raising animals to provide quality meat
- tracking – using ear tags to track animal health throughout their life
- handling – using a stress free method of moving livestock
Water Analysis
- contamination – to make impure; pollute
- concentration – to increase, as in density; a concentrated substance
- groundwater – water that is under the surface of the ground
- indicator – to be a sign of change
- ppb – parts per billion, a term used to describe parts of a polluting substance per billion drops of water
- source – a place of origin
- spot plate – a tray to hold samples of water or other liquids in an experiment
Corn to Plastic
- biodegradable – readily decomposed or broken down by bacteria
- landfill – a place for burying garbage
- non-renewable – a substance that cannot be renewed or used again
- renewable – a substance that can be renewed or used again
Genetics
- biotechnology – a collection of scientific techniques, including genetic engineering, that are used to create, improve, or modify plants, animals and microorganisms
- chromosome – any of the microscopic bodies carrying the genes of heredity
- DNA – deoxyribonucleic acid basic material of chromosomes that transmits a heredity pattern
- dominate – genetic material that overpowers recessive genes; genetic material that is the stronger trait and are always expressed in the offspring
- gene – a unit of heredity in a chromosome
- genotype – internally coded, inheritable information carried by all living organisms
- inherited – DNA material of both parents that is carried to the offspring
- phenotype – the outward, physical manifestation of the organism; anything that is part of the overall structure, function, or behavior of a living organism
- recessive – genetic material that tends to recede or be diminished
- trait – a characteristic
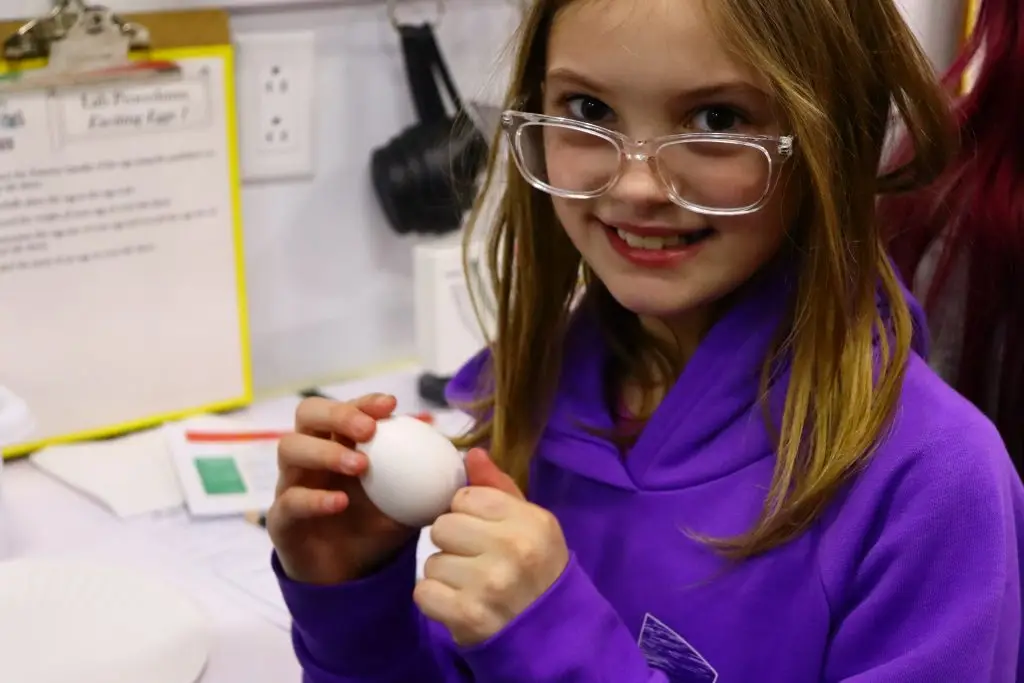
Exciting Eggs
- air cell – a space between the inner and outer shell membranes that increase with time
- albumen – the white part of the egg that acts as an elastic shock absorber and has a high water content
- bacteria – microorganisms causing disease
- candling – a device which is used to judge interior quality by holding the egg up to a light to see the air cell, yolk, and the white
- chalazae – two whitish cords on opposite sides of the yolk which hold the yolk in the center of the albumen
- follicle – a small sac or gland
- germinal disk – a tiny spot on the upper surface of an egg and if fertilization occurs it will develop into an embryo
- oviduct – the organ of a female bird which puts the albumen, shell membrane, and the shell around the yolk
- shell – hard outer covering, as on an egg
- shell gland – a gland that secretes a substance that causes the hardening of egg shells
- shell membrane – two thin layers (outer and inner) inside the shell that surrounds the white albumen portion of the egg
- USDA regulations – United States Department of Agriculture certification that states the eggs have been examined for quality and size
- yolk – the round, yellow mass inside the egg
- yolk sac – the follicle in which an ovum and its surrounding yolk are held until the yolk matures and is released
Bug Out!
- beneficial – helpful or an advantage
- complete – a complete change in form as in a caterpillar to a moth or butterfly, from larvae to
- insect – a small animal with six legs
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM) – IPM is a thoughtful 6 step method of assessment, treatment, and evaluation to ensure the least invasive treatment necessary is used to minimize pest damage while protecting human health, the environment, and economic viability
- metamorphosis – change insects go through from pupa to adult
- methods –
- cultural: site selection, sanitation, plant health, rotations
- physical: tillage, weeding, mulching, pruning, traps barriers, flaming
- biological: predators, parasites, nematodes
- chemical: soaps, oils, baking soda, repellants, microbials, herbicides, insecticides, fungicides
- pest – something that causes annoyance, damage or harm
- vertebrates – having a spinal cord or backbone
Super Slurper
- absorbency – having power, capacity, or a tendency to soak up liquids
- non-renewable – a substance that cannot be renewed or used again
- osmosis – movement of water through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of low
concentration to high concentration - polymer – a naturally occurring or synthetic chemical compound consisting of large molecules made up of millions of repeated linked units
- renewable – a substance that can be renewed and used again
- saturated – unable to hold or contain more; full
- water-holding capacity – the maximum amount of water a given substance can hold before becoming saturated
Banana DNA
- biology – the study of living things
- biotechnology – a tool that uses biology to make new things or improve the products we have
- cell – the basic units of living things
- cell membrane – thin semi-permeable membrane that surroungs the cytoplasm of a cell, enclosing its conents
- chromatin – a protoplasmic substance in the nucleus of a cell that allos ceratin molecules to pass through
- chromosomes – a rod-shaped structure, usualy found in pairs in a cell nucleus, that carries the genes that determine sex and the characteristics an organism inherits from its parents
- cytoplasm – the living part of the cell inside the cell membrane and outside the nuclear membrane, where much of the work of the cell occurs
- DNA – the hereditary material in cells that contains the instruction for producing the cell and enabling it to function
- extract – a procedure to obtain, or remove, a substance by chemical or mechanical action
- filtrate – the material collected after a solution or mixture passes through a filter
- genes – hereditary unit consisting of a sequence of DNA that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and determines a particular characteristic in an organism
- living things – something that is capable of growth, reproduction and metabolism
- nucleus – a membrane-bound structure that contains the cell’s hereditary information and controls the cell’s growth and reproduction
- nuclear membrane – a double-layered membrane enclosing the nucleus of a cell that allows certain molecules to pass through
- precipitate – solid material that comes out of a solution as a result of a chemical or physical change
- slurry – a watery mixture; a liquid mixture of water and an insoluble solid material
- technology – a tool used to make things better
The Science of Chocolate
- cocoa bean – the seed of the cacao plant
- cocoa butter – a fatty substance obtained from the cocoa bean
- cocoa nibs – the center of a cocoa bean that is used to make chocolate
- cocoa powder – powdery remains of chocolate liquor after cocoa butter is removed
- dissolve – to melt of liquefy; to make a solution by mixing with a liquid
- food scientist – a person who studies all aspects of food development, from harvest to development and manufacturing to packaging
- ingredients – any substance that is combined to make a particular product
- melting point – the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid
- palate cleansing – to clean and refresh the mouth of any previous taste between different substances
- solute – something that gets dissolved
- solution – the mixture that results when a solute has completely dissolved in a solvent
- solvent – the substance in which the solute is dissolved
- soybeans – seed of a bushy plant in the legume family that is grown for food, animal feed, and a variety of other uses
- soy lecithin – a yellowish-brown fatty substance extracted from the soybean that is used as an emulsifier in foods to hold ingredients together
- taste test – to try or test the flavor or quality of something by taking some into the mouth
- vanilla pod – the fruit of bean of the vanilla plant
- viscosity – tendency of a liquid to not flow
Primary
Thirsty Stems
- capillary action – the principal characteristic of stems is their ability to move water and dissolved minerals upward, downward, and side-to-side within plants
- flower – petals and pistil of a plant
- leaves – flat, thin, usually green part growing from a plant stem
- root – underground part of a plant
- stem – stalk of a plant or flower
Bee-utiful Relationship
- flower – petals and pistil of a plant
- petal – leaf-like part of a blossom
- pistil – seed-bearing organ of a flower
- pollen – powder-like cells from the anthers of flowers
- pollination – placing pollen on the pistil of a flower
- pollinator – insects that pollinate flowers
- sepal – leaf-like part at the base of a flower
- stamen – pollen-bearing part of a flower
Feast Like a Bug
- beneficial – helpful or an advantage
- harmful – causing hurt or damage
- insect – a small animal with six legs
- labellum – a liplike part, such as the tip of the proboscis of various insects, used for lapping up liquids
- mandible – lower jaw of mammals and some insects
- piercing proboscis – a sharp, straw-like tube on some insects used to gather food
- proboscis – a special, slender mouth part on some insects used to gather food
Popcorn Capers
- corn – a tall green plant that produces large grains, or kernels, set in rows on a cob that yields numerous products that are highly valued for both human and animal consumption
- float -float to stay on the surface of a liquid
- kernel – the seed of a grain
- popcorn – a variety of corn with hard kernels that swell up and burst open with a pop when heated
- seed coat – the protective, outer surface of a seed
- sink – to go or put beneath the surface of the water
Walk-Through
Farm Charm
- barn – farm building used for livestock and storage
- farm – land used to raise crops or animals
- fertilizer – manure or chemicals to enrich the soil
- plants – living things that cannot move and can make its own food
- soil – earth or ground, especially the surface layer
Tops and Bottoms
- flower – petals and pistil of a plant
- fruit – the pulpy, edible product of a plant or tree
- leaves – flat, thin, usually green part growing from a plant stem
- root – underground part of a plant
- seed – the part of the plant from which a new one will grow
- stem – stalk of a plant or flower
- weed – unwanted plant, as in a lawn
Crawly Critters
- abdomen – the part of the insect’s body between the head and thorax
- antennae – the feelers on the head of an insect
- beneficial – helpful or an advantage
- compound eyes – many small eyes within two larger eyes in an insect
- pheromones – substances secreted by animals to signal others of the same species
- thorax – the middle segment of an insect
- wings – organ used by a bird or insect in flying
Little Red Hen’s Pizza
- dairy – milk products such as yogurt, cheese, and milk
- grains – the seed of a food plant such as wheat and corn
- farm – land used to raise crops or animals
- pork – food that comes from pigs
- soil – earth or ground, especially the surface layer
- wheat – a type of grain that can be ground into flour
Forest & Me
- erosion – the process by which the surface of the earth is worn away by the action of water, glaciers, winds, waves, etc.
- windbreak – a growth of trees, a fence, or the like, that serve as a shelter from the wind
- roots – underground part of a plant
- branches – a limb or offshoot of the main stem
- trunk – the main stem of a tree
- leaves – flat, thin, usually green part growing from a plant stem
- oxygen – a colorless, odorless gas that humans and animals breathe (inhale)
- carbon dioxide – a colorless, odorless gas that humans and animals breathe out (exhale)
- photosynthesis – the process by which plants convert the carbon dioxide into their food, with the help of the energy from the Sun.
How Does Your Garden Grow
- air – invisible gas, mostly oxygen and nitrogen, surrounding the earth
- calcium – a mineral nutrient responsible for keeping bones and teeth strong
- chemical symbol – a letter abbreviation for a chemical element
- nutrients – anything that nourishes a living thing; a substance or material used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce
- nitrogen – keeps plants green and healthy
- phosphorous – helps plants grow strong and healthy roots
- potassium – helps plants fight disease
- fertilizer – a chemical or natural substance added to soil to increase its fertility, or ability to grow plants
- soil – the upper layer of the earth
- soil testing – analyzing a sample of soil to determine the nutrient content
- photosynthesis – the process by which plants use sunlight to make food from carbon dioxide and water
- oxygen – colorless, odorless gas found in the air that supports life
Can You Dig It?
- dirt – dead soil with no nutrient value
- soil – a living ecosystem composed of water, air and plant an animal matter
- ecosystem – a community of interacting organisms and their environment
- organic matter – matter that has come from a recently living organism
- bedrock – bottom layer, solid rock
- parent material – mostly weathered or broken rock
- subsoil – made up of sand, silt, clay that has not been broken down all the way
- topsoil – layer that provides support and nutrients to plants; the layer where plants and animals live
- organic layer – thin layer where decomposed parts of plants, leaves and insects can be found
- nutrients – anything that nourishes a living thing; a substance or material used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce
- carbon dioxide – colorless, odorless gas breathed out by humans and absorbed by plants
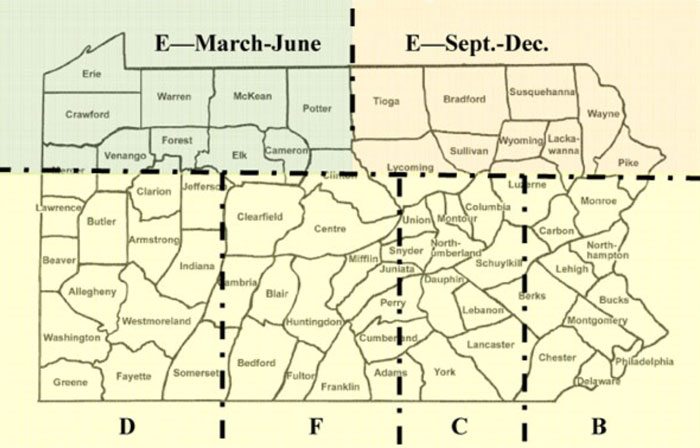
Map
Contact the Ag Lab Program for availability of labs, as additional time slots may be available on our backup lab.
Please Note:
LAB E services two areas of the northern tier of PA during specific dates.
Lab E – Northwestern, PA (March – June)
Lab E – Northeastern, PA (Sept. – Dec.)
Mobile Agriculture Education Lab 2025-26 Schedule
Please note, schedule is subject to change and may not reflect most recent bookings.
Lab A
|
Lab B
| Lab B Scheduled | School | School District | County |
| Sept. 1-5 | |||
| Sept 8-12 | East Fallowfield Elementary | Coatesville Sd | Chester |
| Sept 15-19 | Exton Elementary | West Chester Area SD | Chester |
| Sept 22-26 | Pleasant Valley Intermediate | Pleasant Valley SD | Monroe |
| Sept 29-Oct 3 | Pleasant Valley Intermediate | Pleasant Valley SD | Monroe |
| Oct 6-10 | Moore Elementary | Northampton SD | Northampton |
| Oct 14-17 | Lankenau Environmental | Philadelphia SD | Philadelphia |
| Oct 20-24 | Green Valley Elementary | Wilson SD | Berks |
| Oct 27-30 | Beaumont Elementary | Tredyffrin Easttown SD | Chester |
| Nov 3-7 | Oley Valley Elementary | Oley Valley SD | Berks |
| Nov 11-14 | St Ignatius Regional School | Private | Berks |
| Nov 17-21 | Quarryville Elementary | Solanco SD | Lancaster |
| Nov 24-26 | |||
| Dec 2-4 | Kraybill Mennonite School | Private | Lancaster |
| Dec 8-12 | Friendship Elementary | Southern York SD | York |
| Dec 15-19 | Hold for Inventory | ||
| Jan 5-9 | Hold for Inventory | ||
| Jan 12-16 | West Manheim Elementary | South Western SD | York |
| Jan 20-23 | John R Bonfield Elementary | Warwick SD | Lancaster |
| Jan 27-29 | St Catherine of Sienna | Private | Berks |
| Feb 2-6 | Oak Park Elementary | North Penn SD | Montgomery |
| Feb 9-12 | Kissel Hill Elementary | Warwick SD | Lancaster |
| Feb 17-20 | Lititz Elementary | Warwick SD | Lancaster |
| Feb 23-27 | Tilden Elementary | Hamburg SD | Berks |
| Mar 2-6 | Donegal Primary | Donegal SD | Lancaster |
| Mar 9-13 | Brecknock Elementary | Eastern Lancaster SD | Lancaster |
| Mar 16-20 | Owatin Creek Elementary | Exeter Township SD | Berks |
| Mar 23-27 | Elk Ridge Elementary | Oxford Area SD | Chester |
| Mar 30-Apr 2 | |||
| Apr 6-10 | Fort Zeller Elementary | ELCO | Lebanon |
| Apr 13-17 | Greenwich Lenhartsville Elementary | Kutztown SD | Berks |
| Apr 21-23 | Jackson Elementary | ELCO | Lebanon |
| Apr 27-May 1 | |||
| May 4-7 | Loomis Elementary | Marple Newton SD | Delaware |
| May 11-15 | Reamstown Elementary | Cocalico SD | Lancaster |
| May 18-22 | Hershey Primary | Derry Township SD | Dauphin |
Lab C
| Lab C Scheduled | School | School District | County |
| Sept. 2-5 | South Eastern Intermediate | South Eastern SD | York |
| Sept 8-12 | |||
| Sept 15-19 | |||
| Sept 22-26 | Baresville Elementary | South Western SD | York |
| Sept 29-Oct 3 | Delta Peach Bottom Elementary | South Eastern SD | York |
| Oct 6-10 | |||
| Oct 15-17 | Sporting Hill Elementary | Cumberland Valley SD | Cumberland |
| Oct 20-24 | Lincoln Elementary | Gettysburg Area SD | Adams |
| Oct 27-31 | Ore Valley Elementary | Dallastown Area SD | York |
| Nov 3-7 | New Oxford Elementary | Conewago Valley SD | Adams |
| Nov 10-14 | Gettysburg Montessori | Private | Adams |
| Nov 17-21 | Stewartstown Elementary | South Eastern SD | York |
| Nov 24-26 | |||
| Dec 2-5 | Red Mill Elementary | West Shore SD | Cumberland |
| Dec 8-12 | Hold for inventory | ||
| Dec 15-19 | Hold for inventory | ||
| Jan 5-9 | Hold for inventory | ||
| Jan 12-16 | Northern York Middle | Northern York SD | York |
| Jan 20-23 | Dallastown Elementary | Dallastown SD | York |
| Jan 26-30 | Fawn Area Elementary | South Eastern SD | York |
| Feb 2-6 | Rossmoyne Elementary | West Shore SD | Cumberland |
| Feb 9-12 | John Beck Elementary | Warwick SD | Lancaster |
| Feb 16-20 | |||
| Feb 23-27 | Shrewsbury Elementary | Southern York SD | York |
| Mar 2-6 | Conewago Township Elemetnary | Conewago Valley SD | Adams |
| Mar 9-13 | Loganville-Springfield Elementary | Dallastown SD | York |
| Mar 16-20 | Southern Elementary | Southern York SD | York |
| Mar 23-27 | Northern York Elementary | NorthernYork SD | York |
| Mar 30-Apr 3 | |||
| Apr 7-10 | North Hopewell-Winterstown Elementary | Red Lion Area SD | York |
| Apr 13-17 | Susquenita Elementary | Susquenita SD | Perry |
| Apr 20-23 | W G Rice Elementary | South Middleton SD | Cumberland |
| Apr 27-May 1 | |||
| May 4-8 | York Township Elementary | Dallastown Area SD | York |
| May 11-15 | Iron Forge Elementary | South Middleton SD | Cumberland |
| May 18-22 | Maple Avenue Middle | Littlestown SD | Adams |
Lab D
| Lab D Scheduled | School | School District | County |
| Sept. 1-5 | |||
| Sept 8-12 | |||
| Sept 16-18 | East Forest Elementary | Forest Area SD | Forest |
| Sept 22-24 | West Forest elementary | Forest Area SD | Forest |
| Sept 29-Oct 3 | Oklahoma Elementary | DuBois SD | Clearfield |
| Oct 6-10 | Montessori Regional Charter | Private | Erie |
| Oct 15-17 | William Penn Elementary | Elizabeth Forward SD | Allegheny |
| Oct 20-24 | Johnsonburg Elementary | Johnsonburg SD | Elk |
| Oct 27-31 | Mercer Elementary | Mercer SD | Mercer |
| Nov 3-7 | Conneaut Valley Elementary | Conneautville SD | Crawford |
| Nov 10-14 | |||
| Nov 17-21 | Francis Grandinetti Elementary | Ridgway SD | Elk |
| Nov 24-26 | |||
| Dec 1-5 | |||
| Dec 8-12 | Hold for inventory | ||
| Dec 15-19 | Hold for inventory | ||
| Jan 5-9 | Hold for inventory | ||
| Jan 12-16 | |||
| Jan 19-23 | |||
| Jan 26-30 | |||
| Feb 2-6 | |||
| Feb 10-12 | Portersville Christian | Private | Butler |
| Feb 16-20 | |||
| Feb 23-25 | South Buffalo Elementary | Freeport SD | Armstrong |
| Mar 2-6 | Lenape Elementary | Armstrong SD | Armstrong |
| Mar 9-13 | Elderton Elementary | Armstrong SD | Armstrong |
| Mar 16-20 | Stanwood Elementary | Hempfield SD | Westmoreland |
| Mar 23-27 | Rockwood Elementary | Rockwood SD | Somerset |
| Mar 30-Apr 3 | |||
| Apr 7-9 | Western Beaver Jr/Sr High School | Western Beaver SD | Beaver |
| Apr 13-17 | Fairview Elementary | Western Beaver SD | Beaver |
| Apr 20-24 | HIS Kids Christian | Private | Butler |
| Apr 27-May 1 | |||
| May 4-8 | Tidioute Charter | Private | Warren |
| May 11-15 | West Hills Intermediate | Armstrong SD | Armstrong |
| May 18-22 | Hoover Elementary | Mt Lebanon SD | Allegheny |
Lab E
| Lab E Scheduled | School | School District | County |
| Sept. 1-5 | |||
| Sept 8-12 | |||
| Sept 15-19 | East Berwick Elementary | Berwick Area SD | Luzerne |
| Sept 22-24 | East Berwick Elementary | Berwick Area SD | Luzerne |
| Sept 29-Oct 3 | Blue Mountain Elementary East | Blue Mountain SD | Schuylkill |
| Oct 6-10 | Choconut Valley Elementary | Friendsville SD | Susquehanna |
| Oct 13-17 | Northwest Intermediate | Northwest Area SD | Luzerne |
| Oct 20-24 | Lathrop Street Elementary | Montrose Area SD | Susquehanna |
| Oct 27-31 | Carl G Renn Elementary | East Lycoming SD | Lycoming |
| Nov 3-7 | Ferrell Elementary | East Lycoming SD | Lycoming |
| Nov 10-14 | Susquehanna Community Elem | Susquehanna Community SD | Susquehanna |
| Nov 17-21 | Lake-Noxen Elementary | Lake Lehman SD | Luzerne |
| Nov 24-26 | |||
| Dec 2-5 | Loyalsock Valley Elementary | Montoursville SD | Lycoming |
| Dec 8-12 | Hold for inventory | ||
| Dec 15-19 | Hold for inventory | ||
| Jan 5-9 | Hold for inventory | ||
| Jan 12-16 | |||
| Jan 19-23 | |||
| Jan 26-30 | Cochran Primary | Williamsport SD | Lycoming |
| Feb 2-6 | Pine Grove Area Elementary | Pine Grove Area SD | Schuylkill |
| Feb 10-13 | Line Mountain Middle | Line Mountain SD | Northumberland |
| Feb 16-20 | Columbia County Christian | Private | Columbia |
| Feb 23-27 | GC Hartman Elementary | Southern Columbia SD | Columbia |
| Mar 2-6 | Avis Elementary | Jersey Shore SD | Lycoming |
| Mar 9-13 | Ashkar Elementary | Hughesville SD | Lycoming |
| Mar 16-20 | Montgomery Area Elementary | Montgomery Area SD | Lycoming |
| Mar 23-27 | West Berwick Elementary | Berwick SD | Columbia |
| Mar 30-Apr 3 | |||
| Apr 7-10 | Northeast Bradford Elementary | Northeast Bradford SD | Bradford |
| Apr 13-17 | Troy Intermediate | Troy Area SD | Bradford |
| Apr 20-24 | New Covenant Academy | Private | Tioga |
| Apr 27-May 1 | |||
| May 4-8 | Line Mountain Elementary | Line Mountain SD | Northumberland |
| May 11-15 | North Schuylkill Elementary | Northwest Area SD | Schuylkill |
| May 18-22 | Donald E Schick Elementary | Loyalsock Township SD | Lycoming |
Lab F
| Lab F Scheduled | School | School District | County |
| Sept. 1-5 | |||
| Sept 8-12 | Shamokin Elementary | Shamokin Area SD | Northumberland |
| Sept 15-19 | Shamokin Elementary | Shamokin Area SD | Northumberland |
| Sept 22-26 | Marion Walker Elementary | Bellefonte SD | Centre |
| Sept 29-Oct 3 | East Derry Elementary | Mifflin County SD | Mifflin |
| Oct 7-10 | Spring Creek Elementary | State College Area SD | Centre |
| Oct 13-17 | Alloway Creek Elementary | Littlestown Area SD | Adams |
| Oct 20-24 | Upper Adams Intermediate | Upper Adams SD | Adams |
| Oct 27-31 | Shippensburg Intermediate | Shippensburg Area SD | Cumberland |
| Nov 3-7 | Central Columbia Elementary | Central Columbia SD | Columbia |
| Nov 10-14 | |||
| Nov 17-21 | Juniata Valley Elementary | Juniata Valley SD | Huntingdon |
| Nov 24-26 | |||
| Dec 1-5 | |||
| Dec 8-12 | Hold for inventory | ||
| Dec 15-19 | Hold for inventory | ||
| Jan 5-9 | Hold for inventory | ||
| Jan 12-16 | James Buchanan Middle School | Tuscarora SD | Franklin |
| Jan 19-23 | |||
| Jan 26-30 | Linglestown Elementary | Central Dauphin SD | Dauphin |
| Feb 2-6 | East Juniata Elementary | Juniata County SD | Juniata |
| Feb 9-13 | |||
| Feb 17-20 | Sacred Heart of Jesus | Private | Miffin |
| Feb 23-27 | Mountain View Elementary | Central Dauphin SD | Dauphin |
| Mar 2-6 | Lewistown Elementary | Mifflin County SD | Mifflin |
| Mar 9-13 | Cumberland Valley Christian | Private | Franklin |
| Mar 16-20 | Selinsgrove Intermediate | Selinsgrove SD | Snyder |
| Mar 23-27 | Indian Valley Elementary | Mifflin County SD | Mifflin |
| Mar 30-Apr 3 | |||
| Apr 6-10 | |||
| Apr 13-17 | Corpus Christi Catholic School | Private | Franklin |
| Apr 20-24 | |||
| Apr 27-May 1 | |||
| May 4-8 | Park Forest Elementary | State college SD | Centre |
| May 11-15 | |||
| May 18-22 | Shalom Christian Academy | Private | Franklin |
Curriculum Choices
General
Thank you for considering the Mobile Ag Ed Science Lab program to provide a unique hands-on science experience for your students.
Our goal is to be a valuable resource to assist school districts in meeting the Pennsylvania Department of Education Science Standards. To accomplish this goal, our curriculum is developed to address as many Environment and Ecology Standards, and Science and Technology Standards as possible.
To assist you in selecting a lesson from our curriculum that will best benefit your students, we have created a lesson key that provides you with additional information about the lesson:
- E – environment/resource conservation and care
- FS – food safety
- G – “green” (renewable/nonrenewable)
- N – nutrition
- NR – natural resources
- P – process and production
- ** – food item consumption
- X – Not recommended for classes >26
As agriculture is our food source, we have many lessons that utilize different food products. We do not have any peanut products on our labs, however, some products we use may have been produced in a factory where peanuts were present. If you have students with food allergies and have any questions regarding lesson materials. Please contact us our Executive Director at cmespenshade@pfb.com.
Old MacDonald’s Farm
E | NR
In order to adequately accommodate the abilities and learning needs of all students at the schools we visit, we’ve added a lesson specifically designed for Self-Contained Special Needs Classes. An engaging and interactive retelling of “Old MacDonald Had a Farm” helps students discover what farms have and provide to us. The components of a farm are reinforced as students make a “fan farm” by identifying and placing stickers of each farm item on a fan.
Walk Through
These curricular options are available for Kindergarten to 2nd Grade classes. Instead of a science experiment, they offer a 35 minute hands-on activity introducing basic agricultural concepts and scientific information.
Can You Dig It?
E | NR New
Students will investigate the difference between soil and dirt. Students will hear about the process of bedrock becoming top soil. The students will then become soil scientists and dig for samples of things that can be found in the topsoil layer, matching them to pictures and counting what they find.
Farm Charm
E | G | NR
An engaging conversation leads students to decide what makes up a real farm. Samples of these components of a farm are placed in a mini zip lock baggie and worn around the students’ necks as a reminder.
Tops and Bottoms
NR
Students hear a story of a lazy bear and a smart hare that get involved in a deal that has hilarious consequences. This lively folktale leads to a discussion of plant parts and the parts of a plant that provide our food—tops or bottoms. Students plant seeds of a “tops” or “bottoms” plant to take back to their classroom to observe as it germinates and grows.
Crawly Critters
E
Students learn how to identify insects, as well as recognize that not all insects are pests. Students create their own insect and learn how farmers can sometimes use this knowledge to control insects in their fields without harmful chemicals.
Little Red Hen’s Pizza
NR | P
A popular food, pizza, is traced back to the farm through the telling of a modern version of The Little Red Hen. Students interact with the story through the use of props, then create a pizza charm that traces all the parts of a pizza back to the natural resources from the farm needed to produce them.
The Forest & Me
E | NR
Through a sorting activity, the students learn the many uses and benefits of trees in their daily lives…from the clean air they breathe to the food they eat to the homes they live in. Students then create a charm bracelet that reminds them of what trees need, what they provide, and the important role people play in managing this valuable resource.
How Does Your Garden Grow?
E | NR Updated
Through a “visit” to a pumpkin patch, the students learn about what plants need to grow and produce food for us to eat. Not only do they
discover plants need soil, sun, and water, but also about the importance of nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium. Students then create a charm with water beads that reminds them of all the things plants need in order to grow.
Primary, Grades 1-2
This curriculum offers a full 50- minute, hands-on science experiment designed for students in grades 1-2.
Colorful Bean
E | G | NR | P
grades 2-5*
Investigation and Demonstration
Students are introduced to the scientific method as they experiment to decide if petroleum or soybean based crayons produce the brightest color with the least flakiness and best covering power. Students end the session with a crayon making discussion where each student receives a soy-based crayon.
Thirsty Stems
E
Not recommended for beginning of year 1st grade
In order to answer the problem of how water travels to all parts of a plant, students create a model of a plant, then observe the effects of capillary action. The parts of a plant and their purposes, as well as capillary action, are reinforced with a make and take book.
BEE-utiful Relationship
E
Students are introduced to the importance of pollination and pollinators in the development of the fruits they enjoy. As the parts of a flower are identified, students create a model of a flower.
Feast Like a Bug
E
Students become farmers whose crops have been damaged, who then investigate to determine the guilty insects. The different mouth parts of insects is discussed, then students test each mouth part to determine which parts of a plant, if any, are harmed by each mouth part. A distinction is made between beneficial and harmful insects.
Popcorn Capers
G | NR | P
Students learn about different types of corn and how popcorn is a special type of corn. The properties of popcorn kernels and popped popcorn are compared then used to predict if each item will sink or float. Based on the results, students predict floating ability of other food items, then test their predictions.
Elementary, 3-5
This curriculum offers a full 50- minute, hands-on science experiment designed for students in grades 3-5.
Colorful Bean
E | G | NR | P
grades 2-5*
Investigation and Demonstration
Students are introduced to the scientific method as they experiment to decide if petroleum or soybean based crayons produce the brightest color with the least flakiness and best covering power. Students end the session with a crayon making discussion where each student receives a soy-based crayon.
No Soil? Now What?
E | G | NR | P
With only 1/32 of our earth’s surface available upon which to grow food, how will we feed a world population of 9.2 billion by 2050? Hydroponics, growing without soil, is one possibility. Students will discover the need for alternative growing methods, then create their own hydroponic growing system to test if plants can be grown without soil.
The Mighty Smooth Bean
G | NR | P
Investigation and Demonstration
final observations completed back in the classroom
The Mighty Bean
The power of a soybean is revealed to students as they “plant” a soybean in plaster of Paris. Observations amaze students as the soybean shows its strength.
The Smooth Bean
Soybeans are often referred to as “the magical bean” due to their many uses. Students will learn how soybeans grow and discover the various ways they are used in products they use every day. Students end the session with a take home sample of lip balm made from soybean products.
Glue from Milk
G | NR | P | X
final observations completed back in the classroom
Must have full 50 minutes
Students act as chemists and laboratory technicians as they produce glue from milk and then test the strength of their milk glue against Elmer’s glue using a peel test, tensile strength test, and sheer strength test.
Cream to Butter
N | NR | P | **
Students make butter from creams with varying levels of fat content to discover properties necessary for butter production. They will also learn about enzymes (ex. lactase) in dairy foods. Label reading will be employed.
How Well Do You Wash?
FS
Students apply “germs” to their hands and then perform several hand washing test to determine which method of washing most effectively removes “germs”. Effectiveness of removal is measured with a special “glo-germ” light. The need for clean hands while handling food products and the washing of produce will be stressed.
Snack Attack
N
Students test several popular snack food items for the presence of fat within the snack food. Nutritional labels for all the snack foods are read and the nutritional content of the foods examined in order to determine healthy snack foods.
Tree Story
E | NR
Students are introduced to tree dendrology where they date two tree samples and identify patterns of tree growth. Various parts of the tree and their purposes are identified. Students examine the properties of two similar trees and learn how those properties affect the ways in which the trees can be used.
Where’s the Juice?
N | **
Students taste test four different fruit beverages to determine the amount of juice and sugar contained within the beverage. Nutritional labels are read and students reach a conclusion about the nutritional value of the different fruit beverages.
Pigment Power
N
Using different fruit beverages, students test for the presence of Phytochemicals, naturally occurring plant chemicals that give plants their color and provide health benefits. Students are encouraged to include a variety of fruits and vegetables in their diet to ensure healthy bodies and prevent disease.
Fungi Fun
P
Students will learn to differentiate living things into different kingdoms as they work as plant botanists to identify the parts and their functions, characteristics, and properties of plants and fungi. Students will conduct an experiment to discover how fungi react, as well as complete a dissection of a mushroom.
Environmentally Friendly Farmer
E | G | NR
This STEM based lesson allows students to discover several of the ways farmers have been, and continue to protect the environment and natural resources upon which they grow our food and fiber. Student teams design their own environmentally friendly farm to put the conservation practices about which they learned into action.
Exciting Eggs
FS | N | NR
Students act as egg inspectors after discovering and labeling the parts of an egg. Students make observations of the egg exterior to compare to quality labeling charts, then record data as the eggs are candled, inspected for freshness, weighed, and measured.
Middle School, Grades 6-8
This curriculum offers a full 50- minute, hands-on science experiment designed for students in grades 6-8.
Steering Through the Chute
E | P
Students identify the needs of beef cattle to provide us with byproducts we use in our everyday lives, as well as the animal care to safely transport cattle. Students will be introduced to Temple Grandin and learn about how she was a pioneer in implementing a design to safely transport cattle. In this STEM based lesson, student teams will create their own cattle chutes using the design practices they learned.
Water Analysis
E | NR
An imaginary town is experiencing pollution in some of its wells. Students collect data as they analyze the town’s developments, predict the contamination source, consider cost factors, test the wells, and draw conclusions which are to be presented in written form to the town council. Importance of responsible care of natural resources and proper disposal of waste and their impact on our groundwater is discussed.
Corn to Plastic
E | G | NR | P
Two experiments enable students to better understand the concept of a by-product. One investigation examines the environmental impact of two packing foams: Styrofoam (made from petroleum) and Eco foam (made from corn). The next investigation involves students making plastic from corn and comparing it to plastic made from petroleum.
Genetics
E
Students will learn about dominant and recessive genes and how genetics can determine the type of plant that is grown by creating models of corn DNA using different colored paper clips to signify genes. Applications of food biotechnology will be used.
Exciting Eggs
FS | N | NR
Students act as egg inspectors after discovering and labeling the parts of an egg. Students make observations of the egg exterior to compare to quality labeling charts, then record data as the eggs are candled, inspected for freshness, weighed, and measured.
Bug Out!
E
A discussion of insects leads to the knowledge of beneficial and harmful insects. Integrated Pest Management is explained and students apply its methods to an imaginary field sample in order to determine the course of action that should be taken by the farmer.
Super Slurper
E | G
Students examine the absorbency of several household products, then investigate the water holding properties of a commercial agricultural product and a pure chemical. The results of this experiment are related to new developments in the agricultural industry and also served as a precursor to the development of disposable diapers.
Banana DNA
E
Must have full 50 minutes
Students delve into biotechnology as they conduct an experiment to extract DNA from a banana. Through the process, they will learn the basic cell parts, observe DNA, identify the role of DNA in plants, as well as discover the possibilities biotechnology can provide to us today and in the future.
The Science of Chocolate
NR | P | **
Must have full 50 minutes
Students become food scientists as they conduct various tests to develop an understanding of the properties of chocolate that are essential to chocolate production. The importance of everything in chocolate production from the melting point to ingredient ratios to interaction of ingredients to the viscosity of chocolate are examined.
What to Expect on the Ag Lab
Sponsors

Glatfelter Family Foundation










The Donald B. and Dorothy L. Stabler Foundation


Senator Michele Brooks


